
Chinese Calligraphy 101
A picture is worth a thousand words—but in the Chinese language, the words themselves are pictures.
In Chinese characters, there are only six basic brush (or pen) strokes that, when combined in different ways, reveal different words, or characters, and their meanings. You need some 3,000 characters to read a newspaper, 5,000 to be fluent, and 8,000 if you wish to be a scholar. Overall, some 50,000 unique Chinese characters exist, only a fraction of which are needed for day-to-day communication.
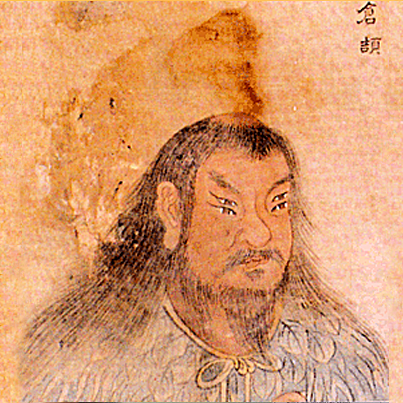

Like clothing, medicine, agriculture, and other elements that constitute China’s “divinely inspired culture,” the written word was regarded as a gift from the gods. The earliest legends are about the inventor of Chinese characters—Cangjie, who lived circa 2,650 B.C.E, almost 5,000 years ago. He also had four eyes, but that’s another story.
As generations and dynasties came and went, those who gracefully wielded this heavenly gift of the written language were revered. Emperors carved their decrees on steles and mountainsides for posterity; statesmen wrote lines of moving verse that started and ended wars; poets painted history in shades of lamentations and praise that were copied and sung long after they, too, were history.
Chinese calligraphy, the art of writing these characters, is a study in four parts: brush, inkstone, ink stick, and xuān (rice) paper. These are also known as the Four Treasures of the Study. It was the mark of educated refinement to have these writing tools—and other supplementary gems such as the brush-holder, paperweights, and seals—on hand.
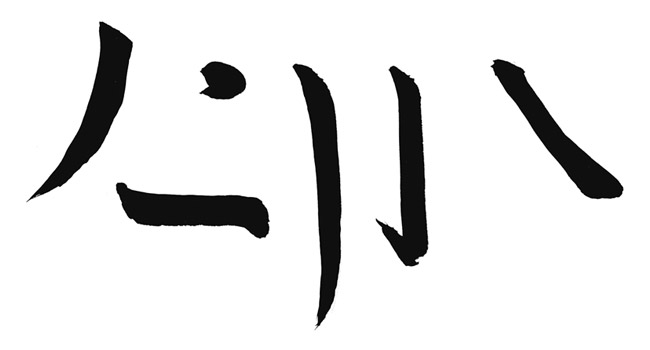
The six basic strokes form the heart of Chinese calligraphy. The héng is a straight line (一) written left to right that also means “one”; two and three, incidentally, are two (二) and three (三) one strokes. The shù is a vertical stroke written top to bottom like a pillar. Piě makes a sweeping stroke from top right to left bottom, a curvy contrast to its opposite partner nà. Their nooks and crannies are quite accommodating to diǎn and tí that dot and trail, respectively, upwards from bottom left. These six strokes go on to combine and form derived strokes, which blend yet again to make more complex words and ideas.
Stroke order is paramount. You can’t approach these symbols any way you want and hope for the best. The bare-bones order for writing a word in Chinese is to move top to bottom, left to right, and outside to inside. Like a well-choreographed dance, a finely written character balances beauty with order. As with much of Chinese philosophy, harmony is the ultimate goal.
Very often, Chinese words have multiple layers of meaning. What in English we call a “word” is in Chinese composed of one or more characters and the character is the sum of its parts: simpler components with basic meanings form complex combinations with greater depth.
For example, “hello” in English is one word, whereas nǐhǎo in Chinese is one word composed of two characters nǐ (你) and hǎo (好). These, in turn, have their own components: nǐ, meaning you, is made of the characters for person (人) and for you (尔); hǎo, meaning good, is made of the two characters woman (女) and child (子). This is one of the simplest examples, but it gets much more complicated and richer (if you’re interested, you can check out our Shen Yun Facebook “Chinese 101” series exploring different characters and their hidden inner-meaning).
Today, you can find two distinct forms of the Chinese written language: simplified (used mostly in mainland China) and traditional (used in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau). The traditional form has, with rare exceptions, preserved the full heritage of the past in its intricate, beautiful strokes—the characters are written today the same way they were thousands of years ago.
And because they date to such an ancient time, a time when it was said that deities walked the Earth and oracles deciphered the will of gods by reading characters on bones, the Chinese script is infused with this divine culture. And it is right there, just beneath the surface still, waiting for us to notice.

Jade Zhan
Contributing writer
2016年5月5日






